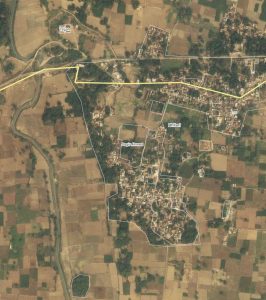
Bhitri (Saidpur, Uttar Pradesh). Satellite view (Wikimapia).
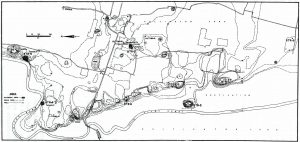
Bhitri (Saidpur, Uttar Pradesh). Site plan showing areas excavated 1968-73 by K K Sinha under the auspices of the Department of Ancient Indian History, Culture and Archaeology, BHU (Zenodo). © BHU.
Bhitri (Ghāzīpur district, Uttar Pradesh). Inscribed pillar as documented in 1870 (Wikicommons).
| Metadata | |
|---|---|
| Object ID | OB00032 |
| Title | Bhitari Pillar of Skandagupta |
| Subtitle | |
| Inscription(s) | IN00036 |
| Child Object | |
| Parent Object | |
| Related Objects | |
| Responsibility | |
| Author | |
| Metadata recorded by | Dániel Balogh |
| Authority for metadata | |
| Metadata improved by | Dániel Balogh |
| Authoriy for improved | |
| Description | |
| Material | Stone / sandstone |
| Object Type | Pillar |
| Dimensions: | |
| Width | 72 |
| Height | 770 |
| Depth | 72 |
| Weight | |
| Details | The pillar is monolithic, consisting of a square base of 2 metres or more in height, a circular shaft (to which the diameter given above applies) 4.7 metres long, and a capital about 1 metre high. The capital is a lotus bell, with a deep narrow socket that presumably held a metal spike that in turn held a sculpture. The upper part of the base is smooth; the lower part is roughly chiseled. |
| History | |
| Created: | |
| Date | |
| Place | Bhitari |
| Other ancient history | |
| Found: | |
| Date | |
| Place | |
| Other modern history | |
| Latest: | |
| Date | 1983 |
| Place | Bhitari |
| Authority | Agrawala, P. K. (1983). Imperial Gupta Epigraphs (गुप्ताधिराजलेखमण्डल). Ancient Indian Epigraphical Sources (प्रत्नाभिलेखसंहिता) X.1. Varanasi, Books Asia. |
| Details | The pillar, but not the inscription, was discovered in 1834 by Tregear in Bhitarī, Ghāzīpur District, UP. The inscription was found by Cunningham after clearing away the earth from the lower section of the shaft. |
| Notes | |
