IN03196 Pālamōṭṭai Slab Inscription
This inscription is engraved on a stone slab, which was discovered by Senarath Paranavitana in 1933. Paranavitana found the slab among the ruins of a Śaiva kōvil at a place named Pālamōṭṭai near Kantaḷāy in the Trincomalee District of the Eastern Province. The architectural style of these ruins suggests that they date from the Poḷonnaruva period – a conclusion which is confirmed by the inscription. The inscription is badly weathered and some letters in the first four lines can only be read conjecturally. Due to the damaged condition of the record, it is difficult to decipher the name of the king in whose reign the record is dated. Senarath Paranavitana initially read the king’s name as Jayabāhu and the regnal year as the eighth (Archaeological Survey of Ceylon Annual Report for 1933, p. 14). However, after consulting with K. V. Subrahmanya Aiyer, Paranavitana revised his reading, taking the king’s name to be Vijayabāhu and the number of the regnal year, which is given in figures, to be forty-two (Epigraphia Zeylanica 4, pp. 192–193). If these readings are correct, the inscription can be assigned to the reign of Vijayabāhu I (r. 1056–1111), although this cannot be accepted with certainty.
The purpose of the inscription is to register donations to the god Śiva in the temple named Teṉ-Kailāsam (the Southern Kailāsam) at Kantaḷāy by a female Brahmin named Nāgaiccāṉi in memory of her husband. The inscription also records that the shrine had the name of Vijayarāja Īśvaram and that Kantḷāy was also called Vijayarāja Caturvedimaṅgalam. The appellation of the shrine suggests that it was founded by or under the patronage of Vijayabāhu I. The chronicles and other inscriptions represent this monarch as a great patron of Buddhism but clearly his zeal for Buddhism did not prevent him from extending his patronage to other faiths practiced by his subjects. The term ‘Caturvedimaṅgalam’ frequently features in South Indian inscriptions, where it is appended to the names of villages inhabited by Brahmins. As it was called Vijayarāja Caturvedimaṅgalam, Kantaḷāy must have had a colony of Brahmins who lived there under the protection of Vijayabāhu I. An inscription of king Niśśaṁka Malla found at the site (IN03105) indicates that Kantaḷāy kept its character as a seat of Brahmins for at least a century longer. In the present inscription, the charitable endowment is placed under the protection of the Veḷaikkāra regiment of Śrī Vikkirama Calāmega. As indicated by the Poḷonnaruva Slab Inscription of the Vēḷäikkāṟas (IN03103), the practice of placing a religious institution and its endowments under the protection of a regiment like the Veḷaikkāras was not unknown.
OB03085 Kantaläi Gal-Āsana Inscription of Kitti Nissaṅka-Malla
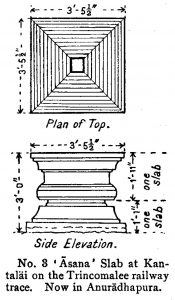
Diagram of the Kantaläi gal-āsana. Published in: Wickremasinghe, Don Martino de Zilva. (1912-27). ‘No. 42. (Reg. No. 3.) Kantaläi Gal-Āsana Inscription of Kitti Nissaṅka-Malla (1187–1196 A.D.),’ Epigraphia Zeylanica 2, p. 283.
IN03105 Kantaläi Gal-Āsana Inscription of Kitti Nissaṅka-Malla
The inscription is engraved around the four sides of a stone seat (gal–āsana), which was discovered in 1921 in the village of Kantaläi on the Trincomalee Railway and afterwards removed to Anurādhapura. The text identifies the stone seat as the one that king Nissaṅka-Malla, after returning from his Indian campaign, used to occupy whilst witnessing the various diversions such as alms-giving, dancing, singing, etc., in the Pārvatī-satra erected at his request in Caturveda-Brahmapura, ‘the city of the Four-Vedic Brahmans’. By way of an introduction, the inscription also includes a bombastic account of Nissaṅka-Malla’s military achievements and charitable acts. Virtually identical accounts are commonly found in other gal-āsana records of this king. The Kantaläi inscription is not dated but, since it references his tours of inspection and his expedition to India, it was probably composed towards the end of his short but eventful reign, which spanned nine years, beginning in 1187 and terminating in 1196. If Kantaläi was the original site of the seat, then this locality must once have been the town called Caturveda-Brahmapura, which was probably occupied mostly by Brahman families for whose benefit an almshouse called Brāhmaṇa-satra was also established by Nissaṅka-Malla.