OB03090 Thūpārāma Slab of Gajabāhu I
IN03110 Thūpārāma Slab Inscription of Gajabāhu I
The inscription is engraved on a stone slab, which was discovered in October 1926 when the foundation of the western side of the enclosing wall of the Thūpārāma in Anuradhapura was cleared. The slab was set up vertically on the inner face of the foundation such that only about one foot (30.48 cm) of the slab would have been visible above the original ground level. The inscription is a grant issued by king Gajabāhu I (r. c. 113 – c.135 A.D.), who is referred to here by the name of Gamiṇi Abaya, as in many of his other inscriptions. The text tells us that the king granted certain incomes derived from the Goṇagiri-utaviya (a tank or a tract of paddy fields) to the monks of the Raṭaṇa Araba monastery. The royal grant ends after the fourteenth letter of the sixth line where traces of two short vertical strokes used as punctuation marks are seen. The rest of the record is in the nature of a postscript added later – but not far removed in time from the original grant, as there is no appreciable difference in the script – to the effect that the city accountant, whose name is not preserved, gave in exchange the water-revenue of the Nakaravavi tank (Nuwara Wewa).
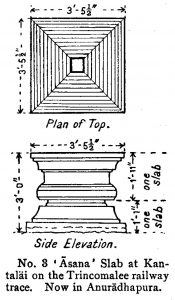
OB03085 Kantaläi Gal-Āsana Inscription of Kitti Nissaṅka-Malla
Diagram of the Kantaläi gal-āsana. Published in: Wickremasinghe, Don Martino de Zilva. (1912-27). ‘No. 42. (Reg. No. 3.) Kantaläi Gal-Āsana Inscription of Kitti Nissaṅka-Malla (1187–1196 A.D.),’ Epigraphia Zeylanica 2, p. 283.
OB03057 Ruvanväli-Dāgaba Slab of Kīrti-Niśśaṅka-Malla
IN03077 Ruvanväli-Dāgaba Slab Inscription of Kīrti-Niśśaṅka-Malla
The inscription is engraved on the side of a fixed slab, which stands erect in a bed of brickwork, flanked by two monolithic pillars, within a few yards of the statues near the eastern altar of the Ruvanväli-dāgaba in Anurādhapura. It was discovered in 1874 by Nāranviṭa Thēra. The inscription consists of 35 lines in the Sinhalese alphabet of the twelfth and thirteenth centuries. It dates from the reign of Kīrti-Niśśaṅka-Malla (1187-1196 A.D.) and gives a general account of his various philanthropic and religious acts, mostly in Poḷonnaruva, his state visit to Anurāpura in his fourth regnal year, the lavish manner in which he worshipped the Ruvanväli-dāgaba there, and the steps he took to restore the Mīrisaviṭiya and other vihāras.
OB03056 Ram̆bǟva Slab Inscription
OB03044 Jētavanārāma Slab of Maḷu-Tisa
IN03064 Jētavanārāma Inscription of Maḷu-Tisa
H. C. P. Bell discovered the present inscription in 1910 in what was then believed to be the Jētavanārāma dāgaba. This dāgaba has since been shown to be part of the Abhayagiri vihara. The record consists of 16 lines of the top side of a slab, which has been reused to form one of the flag-stones of the pavement at the south altar of the dāgaba. Written in the Southern Brāhmī alphabet of the latter part of the 2nd or the first half of the 3rd century A.D., it records donations from the king Maḷu-Tisa to the Utara-maha-ceta, identified with the Abhayuttara-mahā-cētiya of the Abhayagiri-vihāra, as well as water regulations.
OB03042 Jētavanārāma Slab 2 of Mahinda IV
IN03062 Jētavanārāma Slab Inscription 2 of Mahinda IV
The inscription is engraved on a slab found lying what was at the time believed to be the Jētavanārāma area, not far from the ‘stone canoe’ (trough) on the outer circular road in Anurādhapura. This area has since been shown to be the Abhayagiri monastery complex. The slab appears to have been erected very soon after a similar inscribed slab (IN03061) found in the same area. The present inscription consists of 60 lines in the Sinhalese alphabet of the 10th and early 11th centuries A.D. The middle part of the slab is damaged, rending the inscription is largely illegible from line 6 to line 39. The inscription does include a date but, due to the damaged condition of the slab, the year – tentatively read by Wickremasinghe as the eighth of Mahinda’s IV’s reign – is unclear. The text starts with a short account of Mahinda IV and his charitable works. It then deals principally with the regulations instituted by Mahinda IV at the Abhayagiri-vihāra soon after completing the reparation of the dāgaba and other buildings attached to the monastery. The stone statue of Buddha mentioned in line 45 of the inscription may be the same as the one that was seen by the Chinese pilgrim Fâ-hien at the Abhayagiri-vihāra when he visited Ceylon in the 5th century A.D.